Hur inträffar dåliga eller mörka fläckar på skärmen?
2025-05-11
Many customers often encounter bad or dark spots on the display screen. How do bad spots occur? Here is a popular science today:
The causes of bad spots on the display screen can be summarized into the following three categories:
1. Manufacturing process defects
A. Transistor damage
The LCD screen controls each pixel through an independent transistor. If the transistor fails during production or use, the corresponding pixel will not be able to display the color normally.
B. Impurity contamination
If there is dust or tiny impurities attached to the liquid crystal layer, filter and other components during the production process, it will cause the pixel circuit to short or open.
C. Material and process defects
Substandard liquid crystal material quality, insufficient polarizer accuracy or deviation in process parameter (such as temperature/pressure) control may cause bad spots.
D. Dust on the backlight material, or dust when attaching the polarizer, and dust on the display when assembling the backlight, bad spots and dark spots will also appear.
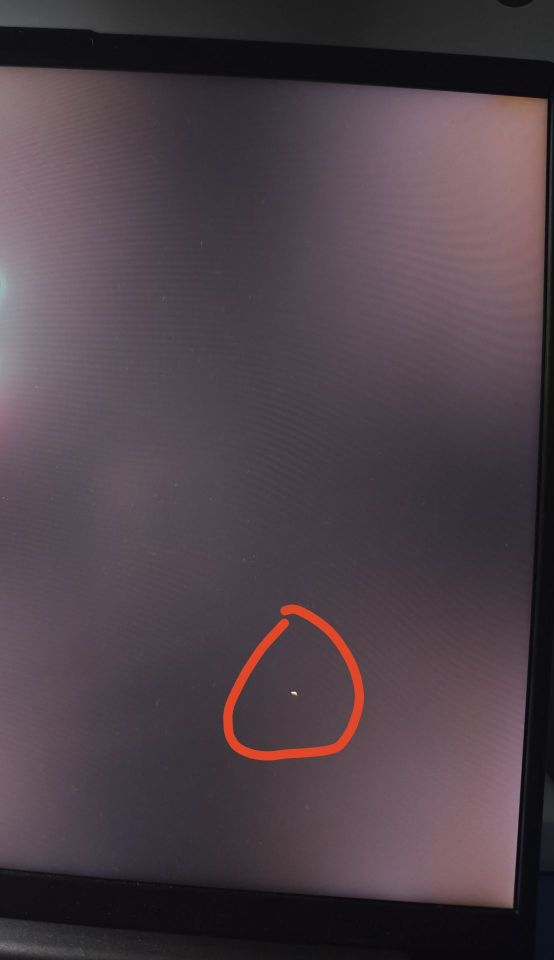

2. Improper use factors
A, External force damage
When the screen is squeezed, hit or placed with heavy objects, the internal crystal structure may be damaged to form bad pixels;
B, Electrostatic interference
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can easily destroy the electric field positioning system of the capacitive screen, resulting in pixel abnormalities;
C, Environmental and operational impacts
Long-term high-load operation, high temperature and humid environment, and the use of corrosive cleaning agents will accelerate component aging and increase the risk of bad pixels.
3. Differences in quality standards
According to the standards for shipment in the display industry, generally bad pixels are shipped at ≤0.2. There are very few displays with bad pixels in a batch of goods. If the customer has requirements for bad pixels, they can also be shipped at the standard of zero defects, that is, there is no bad pixel. Different manufacturers have different quality control standards for the number of bad pixels. Some low-end products allow a certain number of bad pixels to be shipped, while high-end products use more stringent screening standards.
 Svenska
Svenska English
English Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Polski
Polski 한국어
한국어 magyar
magyar Malay
Malay বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi हिन्दी
हिन्दी


